Lithological mapping of magmatic rocks from Mt. Timna, Southern Israel, based on hyperspectral DAIS data analyses
Introduction:
The goal is the investigation of the DAIS 7915 data towards their potential to detect area wide the lithology (mostly magmatic rocks) of the Mount Timna. This investigation was performed within the scope of the projekt - Integrated Quantitative Remote Sensing of Natural Surfaces in the Dead Sea Rift (DSR) Using the Hyperspectral DAIS-7915 Sensor 1997 Data - founded by the German Israeli Foundation for Scientific Research and Development (GIF), which supports the scientific teamwork between several israeli and german departments of geoscience.
Following departments were involved beside the GFZ :
- The Department of Geography of the Tel Aviv University (TAU), Israel,
- The Geological Survey of Israel (GSI),
- The Department of Geophysics and Planetary Sciences of the Tel Aviv University (TAU), Israel,
- The Working Group Remote Sensing of Munich University (AGF) , Germany,
- The Department of Optoelektronic of the German Aerospace Center (DLR), Germany
Test area:
The Mount Timna builds up the center of Timna Valley, which can be assigned to the Arava Vally, respectively to the Dead Sea Rift (Fig. 1). This Valley is also known as the ancient copper mines of king salomon. It is a half circle area, bounded by steep cliffs (approx. 650 m a.s.l.) and it opens only into the south of the Arava Valley.
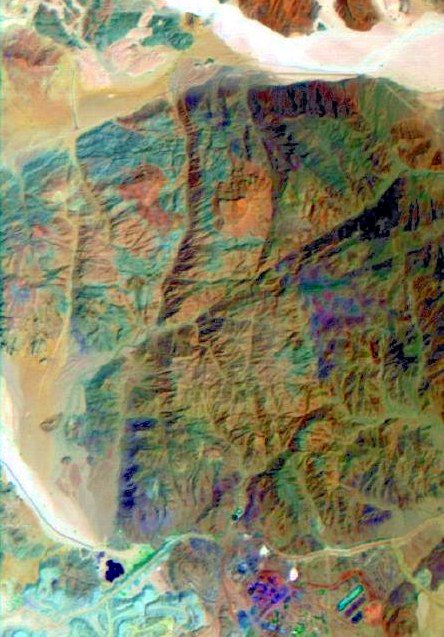
The Mount Timna has an altitude of approx. 400 m and covers an area of 3 km x 5 km (Fig. 2). It is a precambrian, ultramafic to acid plutonic complex. The complex is exposed at the northern margin of the Arabic-Nubien Shield and was generated in the last stage of the Pan-African orogenes (620 - 550 Ma). The main rocks of Mount Timna consist of Alkaligranite, Porphyroid Granite, Quartz Monzodiorite, Monzonite and Diorite. In some places Granodiorite, Olivin Norite and Syenite can be found. The whole complex contains several dike swarms, which are mainly rhyolites and andesites.
Data acquisition und data preprocessing:
The image data of Mount Timna were recorded at the 31.07.1997. This flight campagne was carried out within the scope of a DAIS-LSF-campagne. Figure 3 shows the main part of Mount Timna with an extension of 637 x 444 Pixel and a pixelsize of about 7 m.
Due to the data quality an data enhencement was performed by two noise reduction approaches. Additionally an atmospheric correction was carried out to transform radiance data into reflectance data.
- The first noise reduction approach included the elimination of an apparently systematic horizontal stripe pattern. Therefore a custom elimination technique was carried out.
- The second noise reduction approach was a minimizing of random noise by a maximum noise function Transformation (MNF-Transformation).
- The atmospheric correction approach was performed applying the emperical line method.